The Plain of Catania, known in Italian as “Piana di Catania,” is a vast and fertile expanse of land located in eastern Sicily. This expansive plain, stretching over 482 square kilometers, is not only the largest in Sicily but also one of the most agriculturally significant areas in the entire Mediterranean region. With its rich history, unique geography, and vital role in Sicily’s economy, the Plain of Catania offers a fascinating subject for exploration.
Geographical Features and Formation
The Plain of Catania is situated between the Ionian Sea to the east and the Sicilian hinterland to the west. It is bordered by the Etna volcano to the north and the Hyblaean Mountains to the south. This geographical positioning has played a crucial role in shaping the plain’s characteristics over millennia.The formation of the Plain of Catania is primarily attributed to the continuous accumulation of debris from three major rivers: the Simeto, Dittaino, and Gornalunga. These rivers, flowing down from the surrounding mountains, have deposited sediment over thousands of years, creating a rich alluvial soil that is ideal for agriculture. The Simeto River, in particular, is the second-longest river in Sicily and has been instrumental in shaping the plain’s landscape.Source

Historical Significance
The Plain of Catania has been a center of human activity and agricultural production since ancient times. Its fertile soil and strategic location have made it a coveted territory throughout history. Greek colonists, who founded the city of Catania in the 8th century BCE, were among the first to extensively cultivate the plain.Throughout the centuries, various civilizations, including the Romans, Arabs, and Normans, have left their mark on the plain, introducing new crops and agricultural techniques. The Arab period, in particular, saw significant advancements in irrigation systems, which greatly enhanced the plain’s productivity.
Agricultural Importance
Today, the Plain of Catania remains one of the most important agricultural regions in Sicily and Italy as a whole. Its fertile soil, combined with the Mediterranean climate, creates ideal conditions for a wide variety of crops.
Key Crops
- Citrus Fruits: The plain is renowned for its citrus production, particularly oranges. The famous Sicilian blood oranges, known for their distinctive color and flavor, are primarily grown in this region.
- Cereals: Wheat and other grains have been staple crops in the plain for centuries.
- Vegetables: A wide variety of vegetables are grown, including tomatoes, eggplants, and peppers.
- Olives: Olive groves are a common sight in the plain, producing high-quality olive oil.
- Grapes: Vineyards in the region contribute to Sicily’s wine production.
The Plain of Catania’s agricultural output plays a significant role in Sicily’s economy, providing both for local consumption and export.Source
Irrigation and Water Management
The success of agriculture in the Plain of Catania heavily depends on effective water management. The region has a complex network of irrigation systems, some of which date back to ancient times. The main water sources for irrigation are the rivers that cross the plain and the numerous reservoirs in the surrounding areas.However, in recent years, the plain has faced challenges related to water scarcity. Climate change and periods of drought have put pressure on water resources, leading to concerns about the sustainability of current agricultural practices.Source
Environmental Concerns and Conservation Efforts
While the Plain of Catania is primarily known for its agricultural productivity, it also includes areas of significant ecological importance. The Simeto Oasis, located where the Simeto River meets the Ionian Sea, is a protected nature reserve that provides habitat for numerous bird species and other wildlife.Conservation efforts in the plain focus on balancing agricultural needs with environmental protection. This includes initiatives to reduce water usage, promote sustainable farming practices, and preserve biodiversity.Source
Climate Change and Future Challenges
Like many agricultural regions worldwide, the Plain of Catania is facing challenges related to climate change. Rising temperatures and changing rainfall patterns are affecting crop yields and forcing farmers to adapt their practices.Some of the challenges and adaptations include:
- Water Scarcity: Droughts are becoming more frequent, leading to water shortages for irrigation. This has prompted efforts to improve water efficiency and explore alternative water sources.
- Crop Selection: Some farmers are experimenting with new crops that are better suited to warmer temperatures and require less water.
- Pest Management: Changing climate conditions are altering the patterns of pest infestations, requiring new approaches to pest control.
- Soil Conservation: Efforts are being made to prevent soil degradation and maintain soil fertility in the face of changing environmental conditions.
The Plain of Catania and Catania City
The Plain of Catania is intrinsically linked to the city of Catania, which lies at its eastern edge. Catania, the second-largest city in Sicily, serves as a major economic and cultural hub for the region. The city’s port plays a crucial role in exporting agricultural products from the plain to markets across Italy and beyond.The relationship between the city and the plain is symbiotic. While the plain provides food and economic opportunities for the city, Catania offers processing facilities, transportation infrastructure, and a market for agricultural products.Source
Cultural Impact
The Plain of Catania has significantly influenced the culture and traditions of the region. The agricultural way of life has shaped local customs, festivals, and cuisine. Many traditional Sicilian dishes feature ingredients grown in the plain, and local food markets, such as the famous fish market in Catania, showcase the region’s agricultural bounty.The plain’s landscape has also inspired artists and writers throughout history, featuring in numerous works of literature and art that capture the beauty and significance of this fertile land.Source
Tourism and Agritourism
While not traditionally a major tourist destination compared to other parts of Sicily, the Plain of Catania is seeing growing interest in agritourism. Visitors can experience farm stays, participate in harvest activities, and learn about traditional farming methods.The plain’s proximity to major attractions like Mount Etna and the city of Catania makes it an interesting stop for tourists interested in exploring Sicily’s agricultural heritage.
Research and Innovation
The Plain of Catania is not just a place of traditional agriculture; it’s also a site of agricultural innovation and research. The University of Catania and other research institutions conduct studies on crop improvement, sustainable farming practices, and climate adaptation strategies.Some areas of focus include:
- Developing drought-resistant crop varieties
- Improving irrigation techniques to conserve water
- Exploring new crops that could thrive in changing climate conditions
- Implementing precision agriculture techniques to optimize resource use
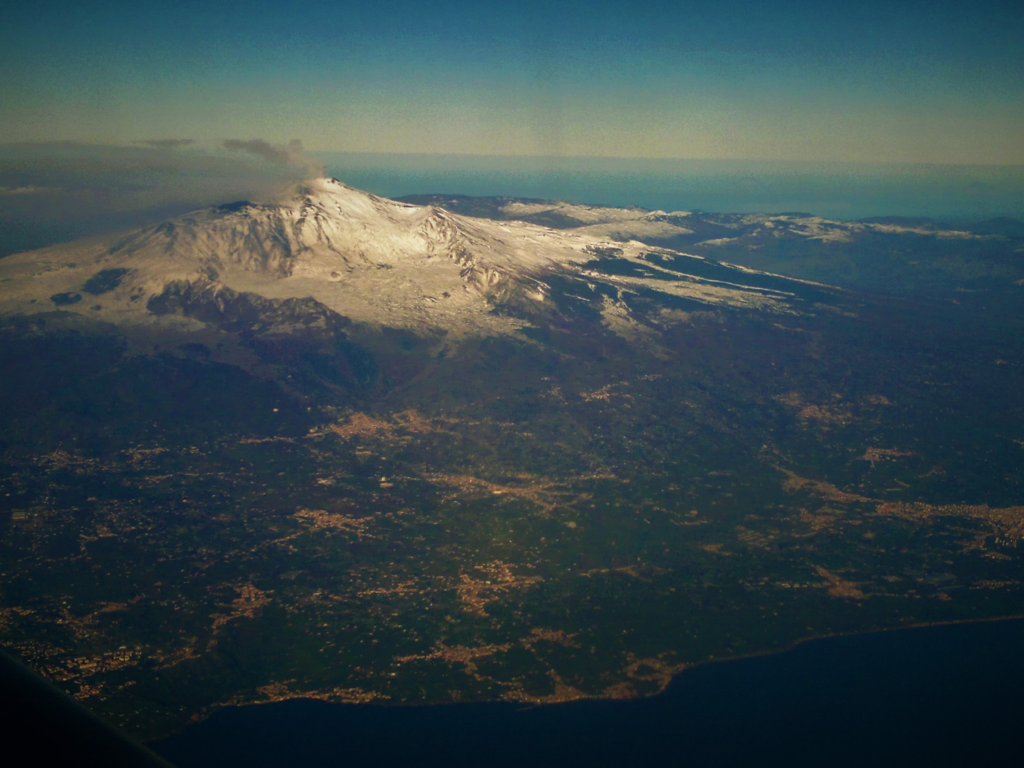

Conclusion
The Plain of Catania stands as a testament to the enduring relationship between humans and the land. For thousands of years, this fertile expanse has nourished civilizations, shaped cultures, and provided sustenance to countless generations. As it faces the challenges of the 21st century, particularly those posed by climate change, the plain serves as a microcosm of the broader issues facing agricultural regions worldwide.The future of the Plain of Catania will likely be defined by how successfully it can adapt to changing environmental conditions while maintaining its agricultural productivity. This will require a delicate balance of preserving traditional practices, embracing innovation, and prioritizing sustainability.As Sicily’s agricultural heartland, the Plain of Catania is more than just a geographical feature; it’s a living, evolving landscape that continues to play a vital role in the island’s economy, culture, and identity. Its ability to adapt and thrive in the face of new challenges will be crucial not only for Sicily but as a model for agricultural regions around the Mediterranean and beyond.The story of the Plain of Catania is far from over. As it has for millennia, this remarkable landscape will continue to evolve, adapt, and sustain life, remaining an integral part of Sicily’s natural and cultural heritage for generations to come.