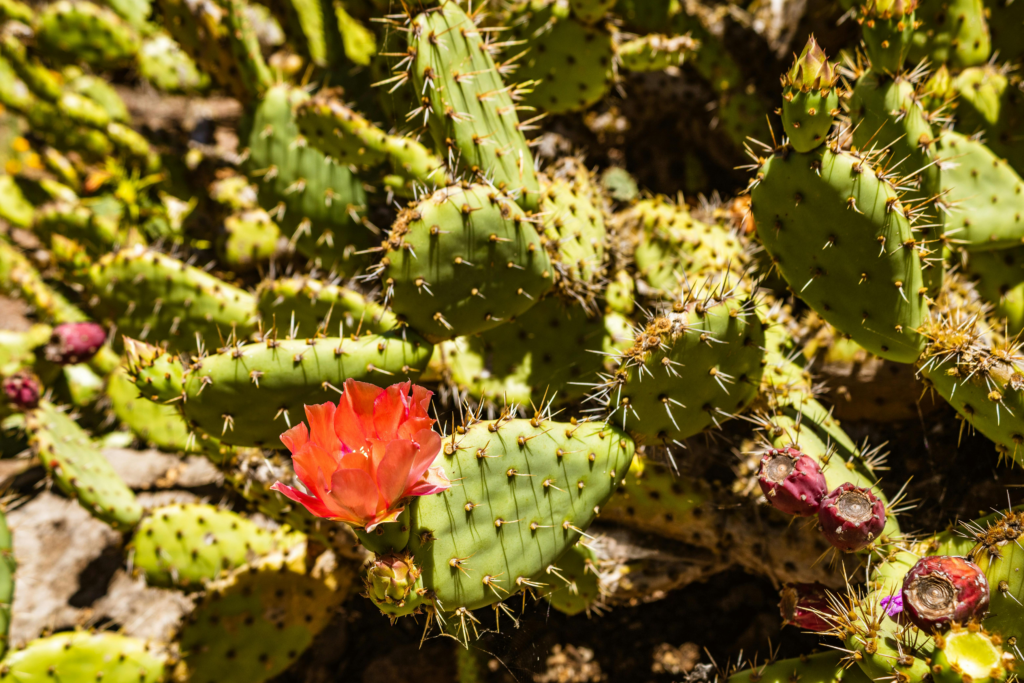
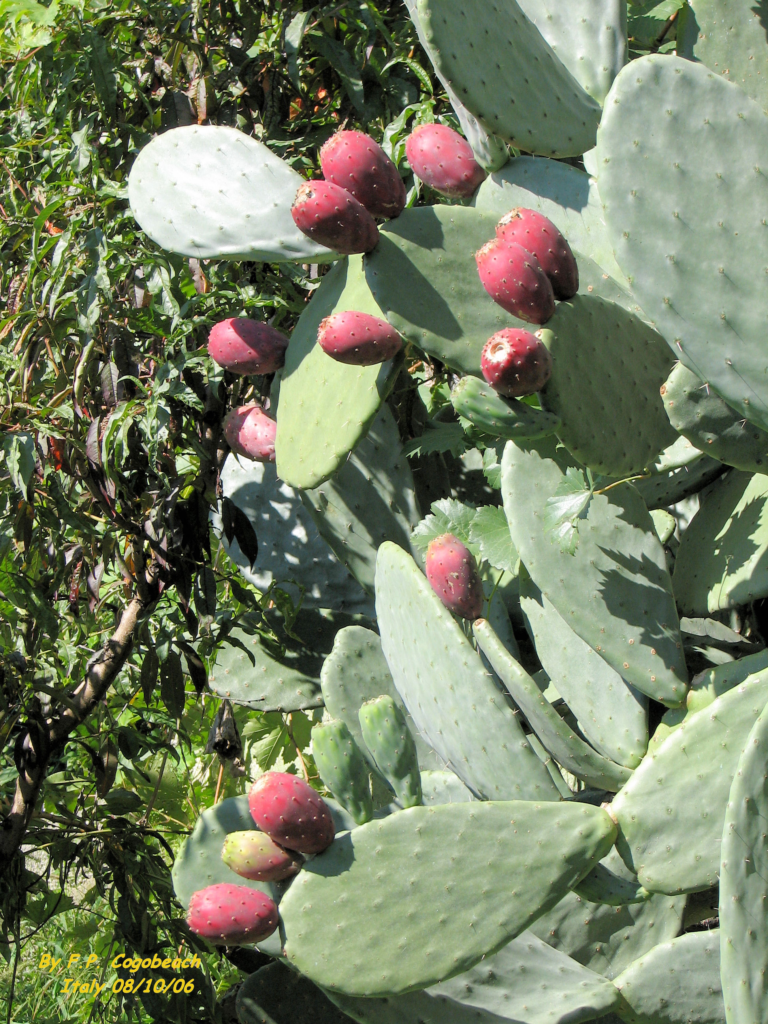
The prickly pear, also known as the Indian fig or Opuntia ficus-indica, is a unique and versatile fruit that has been a staple in Mexican cuisine and traditional medicine for centuries. This article explores the rich history, nutritional profile, health benefits, and culinary uses of this remarkable cactus fruit.
Historical Background and Origin
The prickly pear cactus is native to Mexico and has been cultivated for thousands of years. It played a significant role in Aztec culture and was even featured on the coat of arms of Tenochtitlan, the Aztec capital that later became Mexico City. The Spanish conquistadors introduced the plant to Europe and other parts of the world, where it has since naturalized in many Mediterranean and arid regions.Source
Botanical Description
The prickly pear is the edible fruit of the Opuntia cactus genus. The plant is characterized by its flat, paddle-shaped stems called nopales or pads. The fruit, known as tuna in Spanish, grows on top of these pads and can vary in color from green to red, purple, or yellow-orange. The fruit’s exterior is covered in small, hair-like spines called glochids, which must be carefully removed before consumption.Source

Nutritional Profile
Prickly pears are a nutritional powerhouse, packed with essential vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants. One cup (149 grams) of raw prickly pear contains:
- Calories: 61
- Protein: 1 gram
- Fat: 1 gram
- Carbohydrates: 14 grams
- Fiber: 5 grams (19% of the Daily Value)
- Magnesium: 30% of the Daily Value
- Vitamin C: 23% of the Daily Value
- Potassium: 7% of the Daily Value
- Calcium: 6% of the Daily Value
The fruit is also rich in antioxidants, including phenolic acids, flavonoids, and pigments, which contribute to its potential health benefits.Source
Health Benefits
1. Blood Sugar Regulation
Prickly pear has shown promise in helping to regulate blood sugar levels, making it potentially beneficial for people with type 2 diabetes. The fruit’s high fiber content and unique compounds may help slow the absorption of sugar in the stomach and intestines.Source
2. Cholesterol Management
Studies have suggested that prickly pear may help lower cholesterol levels. The fruit’s pectin content and other compounds may contribute to reducing both plasma and hepatic cholesterol levels.Source
3. Weight Management
The high fiber content of prickly pear can aid in weight management by promoting feelings of fullness and reducing hunger pangs. Additionally, the fruit may help in the elimination of dietary fat by binding to it and facilitating its excretion from the body.Source
4. Antioxidant Properties
Prickly pear is rich in antioxidants, which help protect the body against oxidative stress and may reduce the risk of chronic diseases. The fruit’s betalains, flavonoids, and phenolic compounds contribute to its antioxidant capacity.Source
5. Hangover Relief
Interestingly, prickly pear has shown potential in alleviating hangover symptoms. A study found that consuming prickly pear extract before alcohol consumption reduced nausea, dry mouth, and appetite loss associated with hangovers.Source
6. Anti-Inflammatory Effects
The anti-inflammatory properties of prickly pear may help in managing various inflammatory conditions. Its omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids content contributes to these anti-inflammatory effects.Source
7. Skin Health
The high vitamin C content and antioxidants in prickly pear may benefit skin health by promoting collagen production and protecting against UV damage. Some skincare products now incorporate prickly pear seed oil for its potential anti-aging properties.Source
Culinary Uses
Prickly pear is a versatile ingredient in the kitchen, used in both traditional and modern cuisines. Here are some popular culinary applications:
1. Fresh Consumption
The fruit can be eaten raw after carefully removing the skin and seeds. Its sweet, refreshing flavor is often compared to a mix of watermelon and bubblegum.
2. Juices and Smoothies
Prickly pear juice is popular in Mexico and is often used in smoothies or as a base for cocktails.
3. Jams and Jellies
The fruit’s high pectin content makes it ideal for making jams and jellies.
4. Syrups
Prickly pear syrup is used to flavor various desserts and beverages.
5. Candies
In Mexico, prickly pear is often used to make traditional candies and sweets.
6. Salads
The pads of the cactus (nopales) are used in salads, providing a unique texture and flavor.Source
Preparation and Handling
Preparing prickly pear requires caution due to its glochids. Here’s a safe method to prepare the fruit:
- Wear thick gloves to protect your hands.
- Rinse the fruit under cold water to remove any loose glochids.
- Use a knife to cut off both ends of the fruit.
- Make a lengthwise incision through the skin.
- Carefully peel back the skin to reveal the flesh.
- Remove any visible seeds before consuming or processing the fruit.
Potential Side Effects and Precautions
While prickly pear is generally safe for consumption, there are some potential side effects and precautions to consider:
- Digestive Issues: Overconsumption may lead to mild diarrhea, nausea, bloating, and increased stool frequency.
- Hypoglycemia Risk: People taking diabetes medications should monitor their blood sugar levels closely when consuming prickly pear, as it may enhance the blood sugar-lowering effect of these medications.
- Pregnancy and Breastfeeding: Due to limited research, pregnant and breastfeeding women should consult with a healthcare provider before consuming prickly pear in medicinal amounts.
- Surgery Interactions: Prickly pear may affect blood sugar control during and after surgery. It’s recommended to stop using prickly pear at least two weeks before a scheduled surgery.

Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Prickly pear cactus is known for its resilience and ability to thrive in arid conditions. This makes it an important crop in regions facing water scarcity and soil degradation. The plant’s ability to grow in harsh environments with minimal water requirements has led to increased interest in its cultivation as a sustainable food source and potential biofuel crop.
Conclusion
The prickly pear is a remarkable fruit with a rich history and an impressive array of potential health benefits. From its role in traditional medicine to its growing popularity in modern cuisine and skincare, this cactus fruit continues to captivate researchers and food enthusiasts alike. As we continue to explore its properties and applications, the prickly pear stands as a testament to the untapped potential of many of our planet’s native plants.Whether you’re looking to diversify your diet, explore new flavors, or potentially boost your health, the prickly pear offers a unique and exciting option. As with any dietary change or supplement, it’s always wise to consult with a healthcare professional, especially if you have existing health conditions or are taking medications.The prickly pear’s journey from a staple of ancient Mesoamerican diets to a global superfood highlights the importance of preserving traditional knowledge and continuing to study the potential benefits of plants that have sustained human populations for millennia. As we face global challenges in nutrition, health, and sustainable agriculture, the humble prickly pear may well play a significant role in our future food systems and health practices.