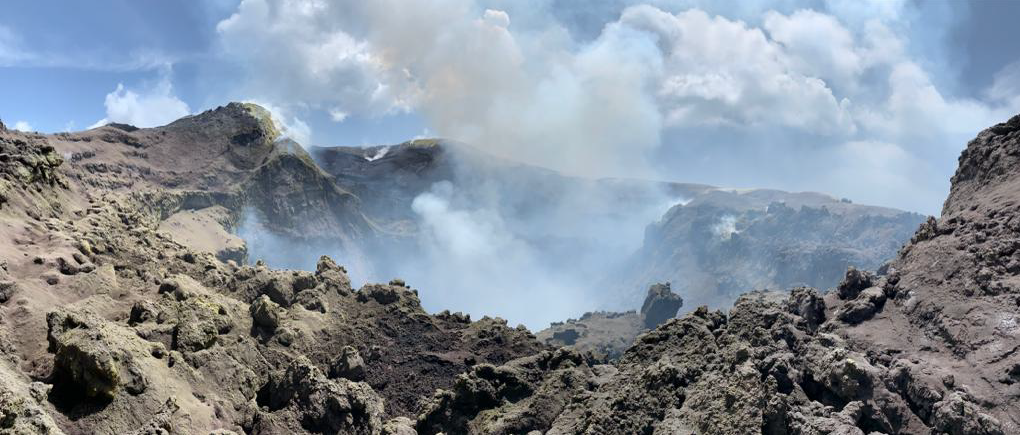
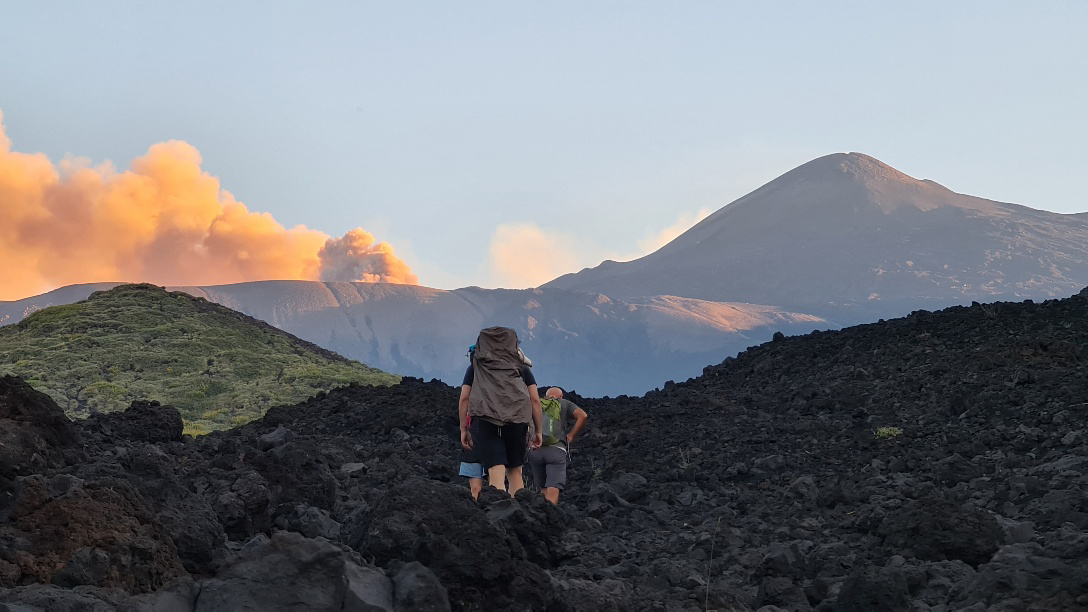
Nestled within the fiery depths of Mount Etna, Europe’s most active volcano, lies a paradoxical wonder – the Grotta del Gelo, or “Cave of Frost.” This unique geological formation stands as a testament to nature’s ability to create seemingly impossible contrasts1.
Location and Formation
The Grotta del Gelo is situated on the northern slopes of Mount Etna in Sicily, Italy, at an altitude of approximately 2,030-2,043 meters (6,660-6,703 feet) above sea level2. This lava tube was formed during a significant eruption between 1614 and 1624, which produced the “lava dei Dammusi” flows on Etna’s western flank2.As the lava flowed, its surface cooled and solidified, creating a crust while the still-molten rock beneath continued to flow. When this underlying lava drained away, it left behind a network of hollow tubes and cavities, one of which became the Grotta del Gelo2.
The Ice Phenomenon
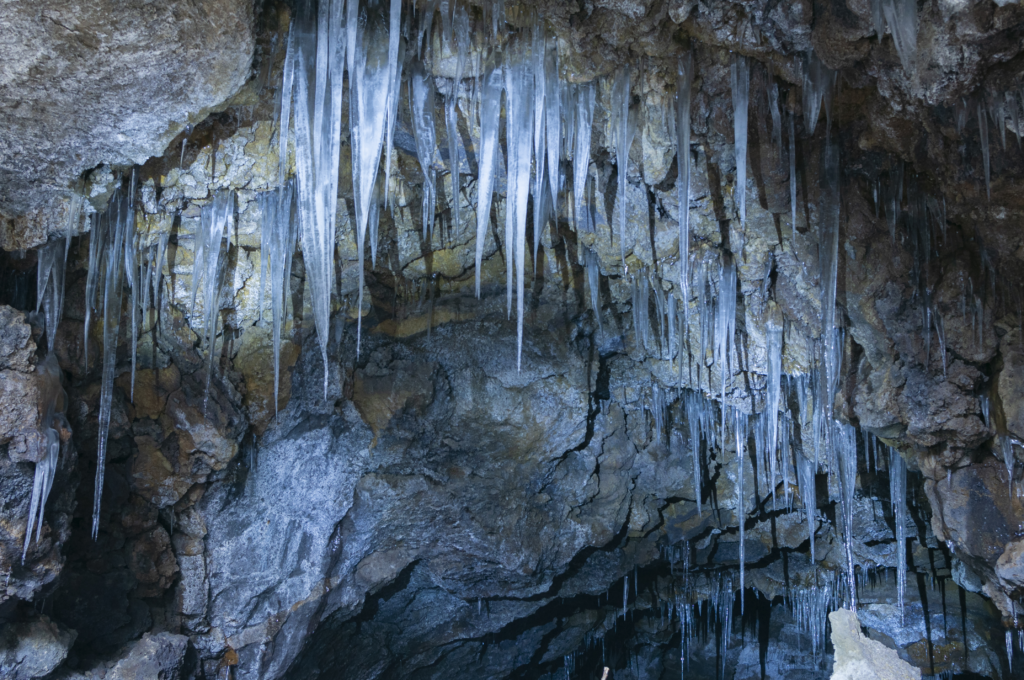
What makes the Grotta del Gelo truly remarkable is its perennial ice formations. Despite being located in the Mediterranean region, known for its warm climate, this cave maintains ice year-round, earning it the distinction of being the southernmost glacier in Europe and the Northern Hemisphere13.The cave’s unique geometry and high altitude contribute to this phenomenon. Cold air becomes trapped within the cave during winter, and when snow melts in spring, the water seeps into the cave and freezes, creating a perpetual ice deposit4.

Cave Description
The Grotta del Gelo extends for about 125 meters into Mount Etna and descends up to 30 meters below the surface4. The cave entrance is approximately 10 by 5 meters wide, leading into a passage about 7 meters in width2.Inside, visitors are greeted by a spectacular display of ice formations, including stalactites, stalagmites, and columns. The cave floor is covered with a thick layer of ice, estimated to be between 1,500 cubic meters2 and 220-260 cubic meters2 in volume.
Scientific Significance
The Grotta del Gelo serves as a valuable site for scientific research. Its ice deposits provide crucial data for studying climate change and volcanic activity5. Scientists analyze the ice composition and monitor temperature and humidity changes within the cave to gain insights into Etna’s volcanic system and its impact on the surrounding environment5.Since the 1980s, researchers have been closely monitoring the cave. In 2013, an improved sensor network was installed to track atmospheric humidity and temperature more accurately2.
Historical Use and Legends
Historically, local farmers used the Grotta del Gelo as a water source for their animals2. Despite being known to locals for centuries, the cave wasn’t systematically documented until the late 20th century. The first known written reference to the cave, as “Bocche de Gelo” (Mouth of Frost), appeared in 18802.Like many of Etna’s volcanic caves, the Grotta del Gelo is the subject of local legends, with tales speaking of hidden treasures within its icy depths2.
Tourism and Exploration
Since the 1970s, the Grotta del Gelo has become a popular attraction for hikers and adventure seekers2. However, accessing the cave requires significant effort and preparation. The journey begins at the Piano Provenzana car park on Etna’s north side, following a path towards Monte Nero4.Visitors are strongly advised to go with experienced local guides and to be properly equipped. Essential items include warm clothing, ice boots, ice axes, ropes, helmets, and adequate lighting4. The best time to visit is in spring when the snow blocking the entrance has melted4.
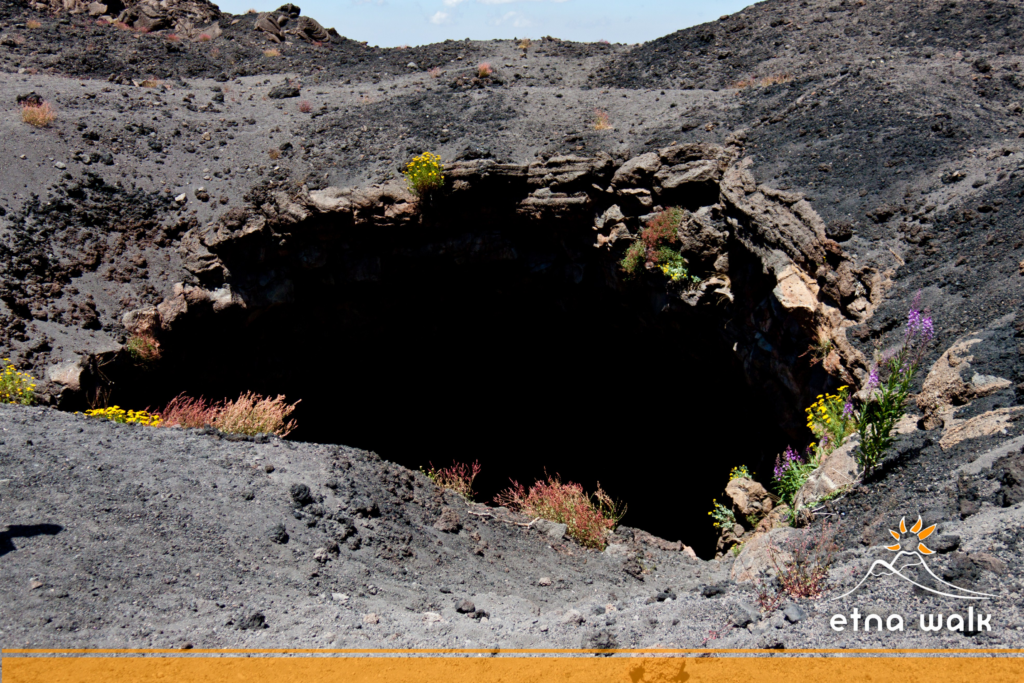

Environmental Concerns
While the Grotta del Gelo has persisted for centuries, it faces challenges in the modern era. Climate change and volcanic activity have impacted the cave’s ice formations. After a period of ice volume increase until the 1980s, the ice mass began to decline due to climate change and a nearby eruption in 1981 that altered the cave’s temperature regime2.However, the ice within the Grotta del Gelo has shown resilience. A phase of increased ice volume was observed during and after 2014, linked to heavy snowfall in the region2.
Conclusion
The Grotta del Gelo stands as a unique natural wonder, offering a stark contrast to the fiery nature of Mount Etna. Its existence challenges our perceptions of what’s possible in nature, providing a frozen oasis within an active volcano.For scientists, it offers invaluable data on climate change and volcanic activity. For adventurers, it presents a challenging yet rewarding exploration. And for all who learn about it, the Grotta del Gelo serves as a reminder of the incredible diversity and complexity of our natural world.As we continue to study and preserve this icy marvel, the Grotta del Gelo will undoubtedly continue to fascinate and educate, offering insights into both Sicily’s geological past and the potential future impacts of our changing climate.